Table Of Content

Treatment for thinning hair will depend on its cause, but may include medications, dietary changes, and more. Most baldness is caused by genetics (male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness). You should also talk with your doctor if you’re worried about persistent hair loss or a receding hairline or if you notice sudden patchy hair loss. Patches of hair loss could signify an underlying medical condition.
Subscribe to Advancing Health

We also treat our community members to special offers, promotions, and adverts from us and our partners. If you don’t like our community, you can check out any time you like. Get the latest news sent straight to your messages by joining our WhatsApp community today. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Causes of Thinning Hair in Men and Women
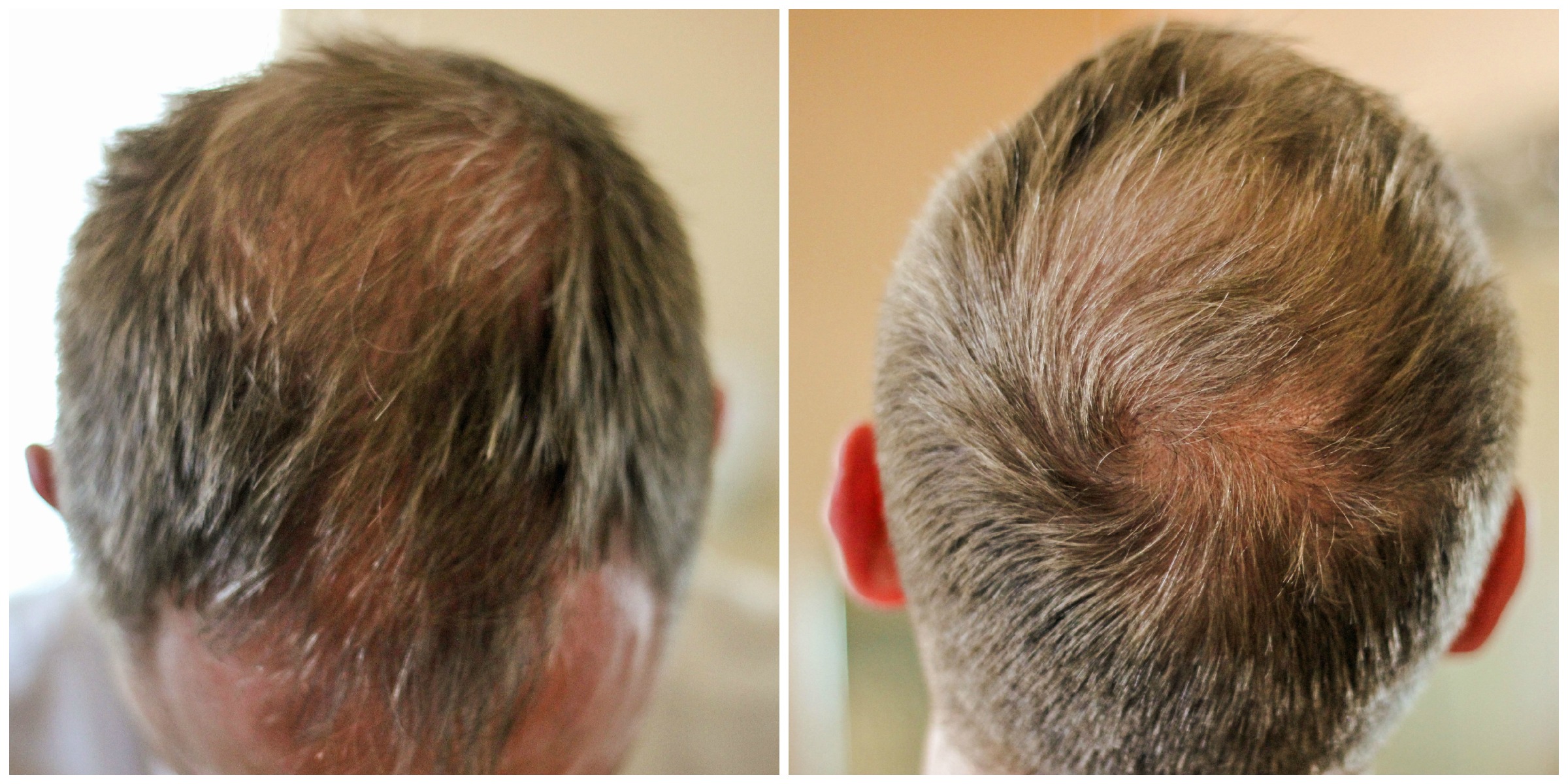
If a person has unexpected and rapid hair loss, they should seek medical advice. The risk of the condition increases with age, but alopecia areata appears on average in people aged 25–36 years. Genetic factors may play a role, and there are links with other autoimmune conditions, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, or lupus. In males, hair thinning tends to occur from the hairline to the back of the head and resembles an “M” shape. According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association, most people lose 50–100 hairs each day, as old hair falls out, and new hair regrows from the same hair follicles.
Medication
In fact, the hair follicles in the hairline are more affected by this kind of hair loss, says Dr. Kobets. Trauma can be physical—like undergoing surgery, pregnancy, extreme dieting, infections, vaccines, and getting in a car accident. It can also be emotional, like losing someone you love or having a high-stress relationship on the rocks. Dr. Kobets adds that this can last anywhere from three to 12 months after the event that caused it, but it can be considered chronic telogen effluvium if it lasts longer than a year. Women with hair loss due to alopecia areata may consider treatment with corticosteroids applied to the scalp or injected into multiple sites in the affected area. People with alopecia areata may also benefit from immunosuppressive medications like methotrexate.
Treatment of this type of hair loss includes therapies such as glucocorticoids, topical immunotherapy, anthralin, or biologic-response modifiers, such as minoxidil. The choice of treatment depends on your age, as well as the extent of hair loss. Milder cases often see a greater improvement with treatment than severe cases. In some cases, the cause of hair loss is obvious — for example, if you're losing hair while going through chemotherapy. Other times, your healthcare provider will need to do some detective work to figure out what’s causing your hair loss. In the type of patchy hair loss known as alopecia areata, hair loss occurs suddenly and usually starts with one or more circular bald patches that may overlap.
Androgenic alopecia causes the normal hair growth cycle to shorten. As a result, hair doesn’t grow as long or thick as it normally would. Stress causes a large number of hairs in the active hair growth (anagen) phase to abruptly enter the resting (telogen) phase. When the hairs reenter the growth phase, the hairs that had been suspended in the resting phase are suddenly released. Hair thinning can occur in certain areas on the scalp, such as the crown or along the part line, leading to noticeable patches or generalized thinning across the entire head.
11 Best Hair Growth Serums to Address Thinning Hair - Vogue
11 Best Hair Growth Serums to Address Thinning Hair.
Posted: Thu, 25 Apr 2024 19:26:30 GMT [source]
Hair Loss Trigger: Thyroid Problems
Taking hormones can change hair growth all over your body. Masculinizing hormone therapy (taking testosterone) may cause hair loss within a year, and the effects aren't reversible if you stop hormone treatment. Hair growth naturally slows with age, so you may notice thinning.
A scalp infection can lead to scaly and sometimes inflamed areas on your scalp. You may see what look like small black dots on your scalp. If you often wear your hair tightly pulled back, the continual pulling can lead to permanent hair loss.
Other Conditions
Sometimes, inflammatory conditions can cause a variety of symptoms, including hair loss. If you eat a balanced diet, it’s unlikely that you’re low in biotin. However, supplemental forms of biotin have been on the rise in recent years, thanks in part to marketers promising more energy and better hair growth with such products. One option for biotin supplements is Hims Biotin Gummies. While the idea of facing your hair thinning head on might feel intimidating, the sooner you address it, the better.
Many people who have plaque psoriasis develop psoriasis on their scalp at some point. A few months after giving birth, recovering from an illness, or having an operation, you may notice a lot more hairs in your brush or on your pillow. This can also happen after a stressful time in your life, such as a divorce or death of a loved one. If you receive chemotherapy or have radiation treatment to your head or neck, you may lose all (or most of) your hair within a few weeks of starting treatment. Free to everyone, these materials teach young people about common skin conditions, which can prevent misunderstanding and bullying. “Lupus of the scalp is another form of scarring alopecia that’s autoimmune,” says Dr. Lenzy.
In their quest to kill cancer cells, both can harm hair follicles and trigger dramatic hair loss. Once your treatment is finished, hair usually grows back. DHT, a derivative of the male hormone testosterone, is the enemy of hair follicles on your head. Simply put, under certain conditions DHT wants those follicles dead. This simple action is at the root of many kinds of hair loss.
Plant-based oils are primary sources of omega-6, while omega-3 fatty acids are found in fish and some seeds. If you don’t normally consume such foods, talk with your doctor about taking a supplement. When you wash your hair, gently apply pressure with your fingertips around your scalp to encourage blood flow. For even more benefits, you can try a handheld scalp massager to also remove dead skin cells. As women, the relationship we have with our hair can be very personal. It can be a form of identity and pride, whether you're rocking thick waves or pin-straight bangs.
Over time, the hairline recedes to form a characteristic "M" shape. Hair also thins near the top of the head, often progressing to partial or complete baldness. In women, the hair becomes thinner all over the head, and the hairline does not recede. It’s also not as common for women with androgenetic alopecia to experience complete baldness.
Advancing age and a family history of the condition are two of the primary risk factors. Below, we’ll explore common causes of hair loss in women and the treatment options available. Some studies show that this procedure can help to stimulate hair growth, especially when used in combination with another treatment, such as minoxidil. These changes happen due to varying levels of hormones during menopause.
Can you tell the difference between hair loss that's temporary and hair loss that needs treatment? Hair loss can also be caused by an imbalance of thyroid hormones or pregnancy, disease, and certain medications, which can all influence hair's growth and shedding phases. Alpha-reductase inhibitors, such as Propecia (finasteride) and Avodart (dutasteride), are additional options for male pattern hair loss. If the stress stops, your body will readjust and the excessive shedding will stop. When the shedding stops, most people see their hair regain its normal fullness within 6 to 9 months. This is a procedure in which your doctor removes hair from a part of your scalp where hair growth is full and implants it into an area where hair is thinning.
JAK inhibitors are a class of drugs that includes Litfulo (ritlecitinib), Olumiant (baricitinib), Opzelura (ruxolitinib), and Xeljanz (tofacitinib). They block signaling pathways that cause inflammation during an overactive immune response. These drugs are approved by the FDA to treat alopecia areata, and some are also approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. If your hair loss results from medication, hormonal imbalances, thyroid disease or diet, your provider will address the cause.

No comments:
Post a Comment